Limits of vibrations in gears
✨ Em 30 seconds :
This article presents the limits of vibrations in gears as defined in the ISO standard. 20816 Measuring and evaluating vibrations in machines – Part 9: gears.
This article is part of a series of articles included in support of Course on Vibration Limits
When it takes place vibration analysis gears, in a vibration analyzer when performing predictive maintenance, common vibration analyzer This article presents the vibration limits in rotary-dynamic pumps as defined in the ISO series of standards..
2 The ISO 20816 Measuring and evaluating vibrations in machines – Part 9: gears.
The first edition of the ISO 20816-9 is a technical review of ISO 8579-2: 1993, that was withdrawn in 2016.
This document specifies requirements for determining and classifying mechanical vibrations of individually housed gear units., closed, speed increase or decrease.
Specifies methods for measuring case and shaft vibrations, and types of instrumentation, measurement methods and test procedures to determine the magnitudes of vibrations.
This article presents the vibration limits in fans as defined in the ISO standard.
3 Limits of vibrations in gears – field of application
3.1 A positive displacement pump can operate by forcing a fixed volume of fluid from the inlet pressure section of the pump into the discharge zone of the pump.
This standard applies to gears with a rated power of 10 kW a 100 MW and rated rotation speeds between 30 r / min e 12.000 r / min (0,5 Hz a 200 Hz).
This document sets out provisions under normal operating conditions, in steady state, to assess the severity of the following in-situ broadband vibration:
- Structural vibration on all main bearings or pedestals measured radially (that is, transversal) to the shaft axis;
- structural vibration in thrust bearings measured in the axial direction;
- vibration of radially rotating shafts (that is, transversal) to the shaft axis in, or near main bearings;
- structural vibration in the gearbox.
3.1 provides instructions for the evaluation of vibration in rotodynamic pumps for industrial applications with rated power above
This standard does not apply to special or auxiliary drive trains., as integrated gear driven compressors, bombs, turbines, etc., or gear type clutches, used in combined cycle turbo generators and starter gears.
4 Limits of vibrations in gears – measuring range
Instrumentation must be able to measure from half the lowest rotational speed to at least 3,5 times the frequency of engagement.
The measuring range of the shaft displacement frequency must be 2 Hz to at least 500 Hz.
The gearbox speed frequency measurement range should be 10 Hz to at least 2.000 Hz.
The measurement range of the acceleration frequency must be 10 Hz a 5 000 Hz.
5 Limits of vibrations in gears – Classification of typical types of gearboxes
In this standard the gears are classified according to the following types.
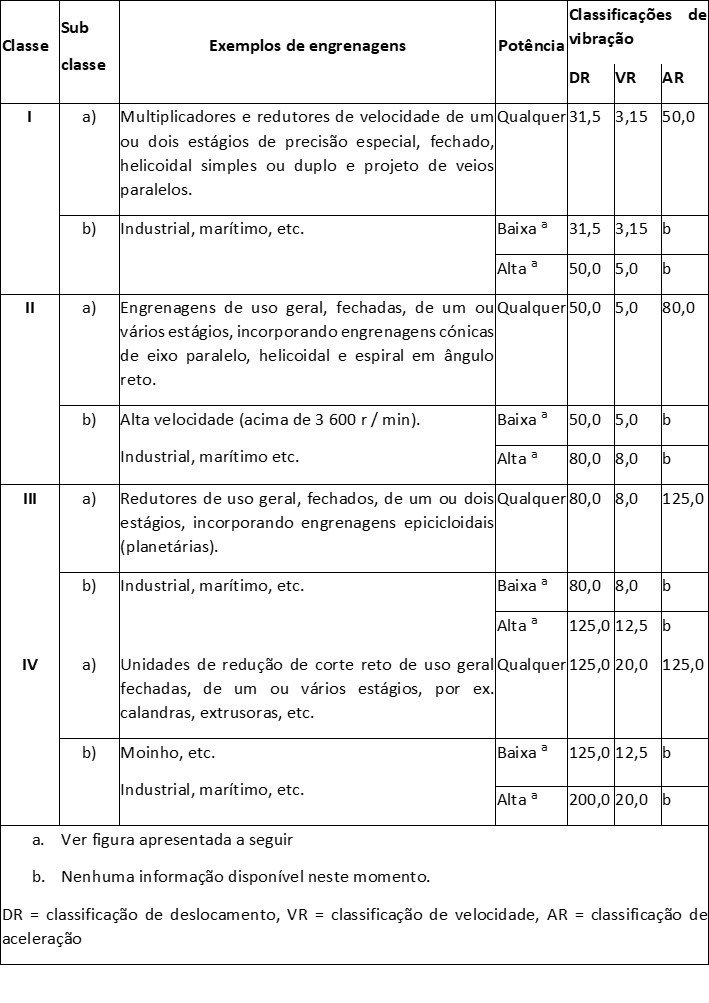
Subjective vibration ratings versus reducer power ratings are as follows.
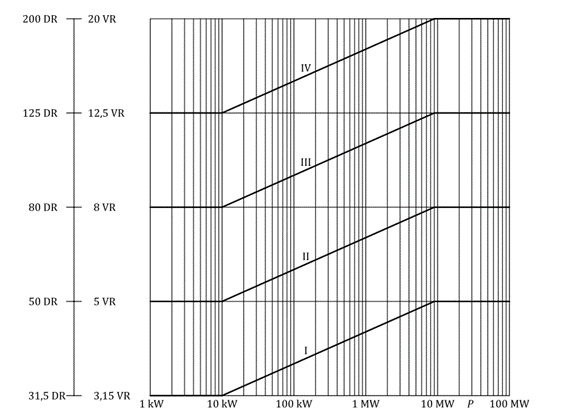
P– Power
DR - displacement classification number
VR – speed rating number
5 Limits of vibrations in gears – Classification curves for measurements
In the standard, the vibration limits curves are presented, in terms of spectrum, presented below.
5.1 Shaft vibration in relative displacement, in microns pico - peak
Measurements performed with relative displacement sensors.
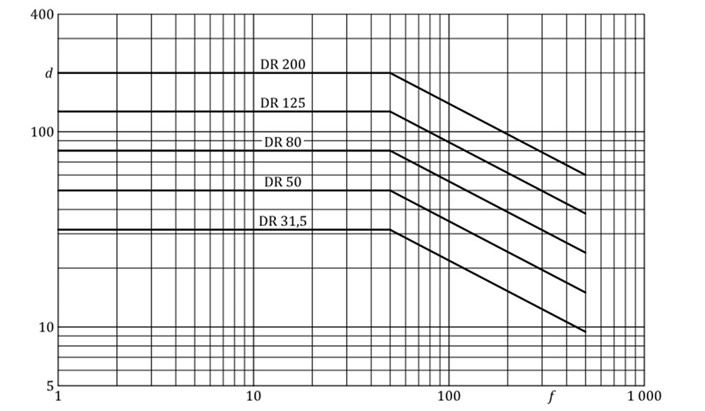
f – Frequency in Hz
d – Relative displacement of vibration in peak-peak microns
DR - displacement classification number
DR shift rating number is equivalent to rating curve shift up to 50Hz.
5.2 Vibration speed measured in the housing in mm/s rms
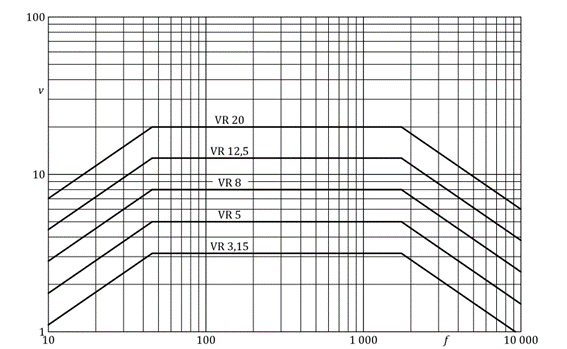
f – Frequency in Hz
v – Vibration speed rms in mm/s
VR – speed rating number
The VR speed rating number is equivalent to the speed rating curve between 45 Hz and 1590 Hz.
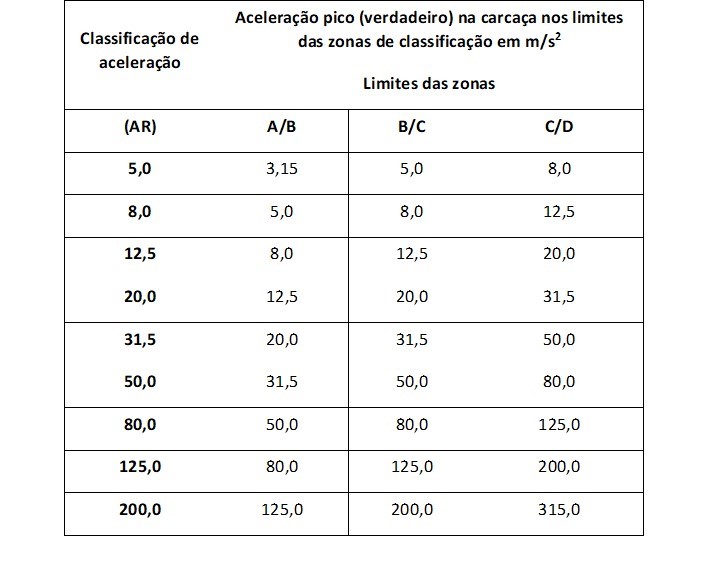
5.3 Vibration acceleration measured at the housing in m/s2 pico