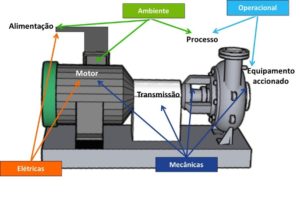
Diagnosis by vibration analysis
This article explains in a general way what the approach to diagnosis by Vibration Analysis.
The diagnosis by vibration analysis is similar to the work of a detective, trying to determine the causes of a crime.
1 – THE WORK OF A DETECTIVE

Just like in a detective’s job, in diagnosis by vibration analysis, there are suspects and clues. De facto, with the help of the available data we have drawn up a list of suspects. parallel, with the help of clues and alibis he tries to eliminate hypotheses until he is left with just one suspect, a coherent history and a set of evidence, all pointing in the same direction. On the contrary, if the real culprit has not been put on the list of suspects, will never find you. On the other hand, if there are not enough leads, an inconclusive situation may arise in which you are unable to determine, with a reasonable degree of certainty, who is to blame. Like this, in this case, the result of your work is a list of likely suspects. Similarly, it can also happen that despite having all the clues, don't reason yourself correctly, and the real culprit is not determined. Thus, in this case, an innocent will be accused.
2 - DIAGNOSIS BY VIBRATION ANALYSIS
De facto, the parallels between diagnostic work and that of a detective are numerous. Like this, when a machine is having problems, the technician who wants to make the diagnosis must have a complete knowledge of the equipment and know all possible causes of the problem. Then, all work is oriented towards eliminating possible causes until, not final, through successive steps, have eliminated all possible causes except one, that will be the cause of the problem. That way, at this point there must be a coherent explanation for what is happening. Likewise, under these conditions there must be no unexplained phenomena. De facto, if this occurs, there is a risk that the cause may be different.
Like this, as in many other things, the vibration analysis diagnostic process can be divided into three phases:
- the before
- the during
- the after
De facto, any of these phases is important and, if they are not carried out correctly, can put down all the effort.
3 – PHASES OF THE DIAGNOSTIC PROCESS BY VIBRATION ANALYSIS
Effectively the elaboration of a diagnosis is a work of educated common sense.
- So it starts with: collect as much data as possible and find as many clues.
- Then proceed to: measurements, tests and confirmations.
- Finally,: elaborating the conclusion and choosing the way to communicate it.
Then, some aspects to be taken into account when making a diagnosis by vibration analysis.
4 – BEFORE MEASUREMENTS
First of all, the objectives of the information gathering phase in the diagnosis by vibration analysis, consist of.
- First elaboration of Classified List of Suspects
- Then follows the immediate determination of culprit. If this is not possible to find the main suspect.
- Finally, prepare the Test Phase
As mentioned, this phase seeks to collect the largest amount of information, and if possible, resolve immediately, the diagnostic problem. It is intended to solve the problem as if the work consisted of an audit.
actually, always bear in mind that this phase is indispensable for the pursuit of work. De facto, you can't jump over it without risking it, later, turns out to be a basic mistake.
In this way, one should proceed as follows:.
4.1 Machine Study
In this phase, the various components of the machine are investigated, tolerances, operating principles, etc. Likewise, the characteristic frequencies are determined.
4.2 Survey of machine history
Like this, in this survey we can see, among others, namely, the following aspects:
- Machine age
- How long have you been working
- What are the initial vibration levels after the last intervention. What is its evolution
- Most common malfunctions
- Recent reviews; who made them; qualification of personnel involved; methods used
At this stage it is very important to talk to everyone involved closely or from a distance with the machine, namely, with the people who operate it. effectively, the bigger the company, the greater the tendency if communication between people is handled in a deficient way. In other words, there is that what is known to some people may not be that of others.
De facto, often someone in the organization, knowing the cause of the abnormal behavior of a machine and the rest of the organization not knowing it.
4.3 Investigation of the Situation
De facto, when performing a diagnosis by vibration analysis, it is common for it to take place because the amplitude of the vibrations is excessive. However, there may be other symptoms of anomaly, that may be relevant to the diagnosis result. It is therefore important to try to identify other symptoms of abnormal behavior.
Beyond this, one should try to infer that other symptoms, beyond vibrations, may cause each anomaly. The purpose of this process is to try to confirm, by alternative methods, the hypotheses elaborated. One should also try to estimate the influence of the different construction aspects of the machine on its vibratory behavior.
4.4 Possible malfunctions and probable malfunctions
Like this, at this point, all possible faults must be kept in mind. If this does not occur, only by chance can the diagnosis be successful. In addition, it is necessary to list and enumerate the probable faults.
That way, at this stage, faults are classified in a decreasing order of probability, in what can be called a “list of suspects”.
Then all the work has the immediate objective of eliminating hypotheses from the list of probable faults until, Lastly, if you only have one.
The example of an electric motor
So see the example of an electric motor. The following figure shows the types of possible failures in an asynchronous electric motor vibrating.

Your list is as follows:
|
List of possible faults |
|
| Mechanical
• Imbalance • Bearings • Days off • Came out bent • Thigh leg • Split leg • Resonance Connection to the driven machine • Misalignment • Coupling in poor condition |
Electric
• Static eccentricity • Dynamic eccentricity • High strength points on the rotor Base • Non-flat base • Massif in poor condition • Loose or broken leg |
Imagine a situation in which vibrations arose after the engine was recently installed on site, by personnel not qualified to carry out alignments.
Under these circumstances, the main cause of the vibrations is the misalignment in the coupling.
4.5 Envision trials to be carried out
Depending on the information collected, it will be envisaged that tests will be carried out and elaborate their procedure.
Taking the example of the electric motor again in the table below, you can see a list of tests and symptoms.
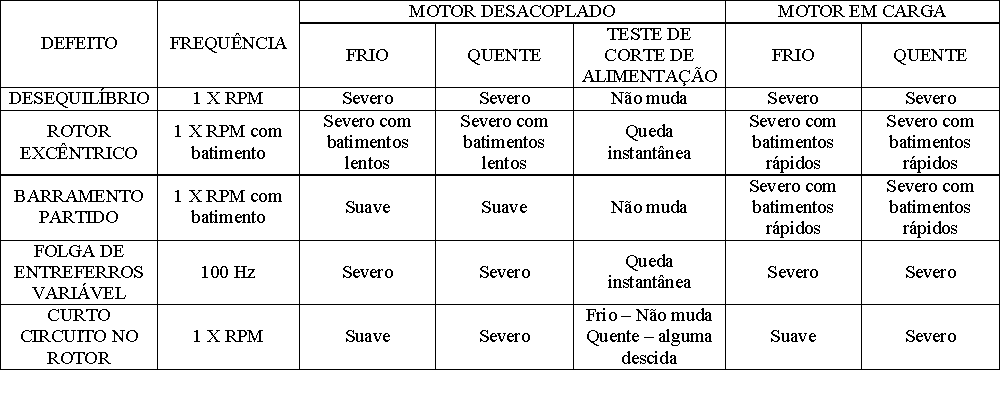
5 MEASUREMENTS IN DIAGNOSIS BY VIBRATION ANALYSIS
First of all, it has to be taken into account that the tests only serve to confirm the suspicions previously raised.
Like this, the objective of this phase is to:
- Firstly, eliminate hypotheses from the Fault List
- Lastly, to be able to stay with only one hypothesis: the culprit
actually, this is the only stage of diagnosis by vibration analysis in which measurement equipment plays a significant role. However, even before they intervene a whole series of preliminaries must take place. That way, then the contact phase takes place.
5.1 Or contact
De facto, before using the vibration analyzer there is, namely, to get an idea, vibrations on the floor, around the machine, components connected to it and its bearings, in the various directions and clamping screws.
The objectives of the contact phase are as follows:
- Determine if the highest amplitudes of vibrations are reached on the machine or, on the contrary, in a close structure.
- Determine which point and direction the machine vibrates the most.
- Perform visual inspection.
5.2 Confirm that the highest amplitudes of vibrations come from the machine.
De facto, before you start looking to determine the cause of a problem on a machine that vibrates excessively, it has to be confirmed that the problem lies in it and not anywhere else.
Like this, therefore, it has to be confirmed that the problem is not linked to:
- Bases and foundations
- Pipes and other structures
- Other machines
For this to be done, we try to confirm that as the distance to the machine increases, the amplitudes of vibrations decrease.
On the contrary, if structures or components are found to vibrate with great amplitudes, it is necessary to suspect from the beginning of resonance in these parts and, hypothesis, this is the source of the vibrations. In these circumstances, first of all, this problem needs to be addressed.
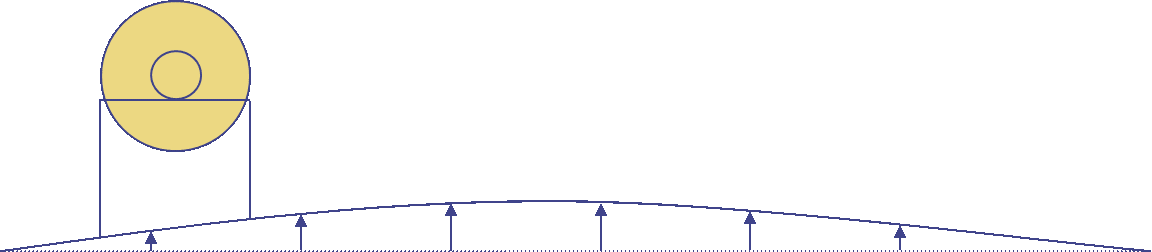
Figure - Take for example the case of the machine on the vibrating platform. De facto, before measuring it on the machine it is not noticed that the soil vibrates more than this, it will be difficult to arrive at a correct diagnosis.
5.3 Determine which point and direction the machine vibrates most
Then, at this stage “palpate” the machine and try to determine at which point and direction it vibrates most. Like this, this can be done with a Global Vibration Level meter or, pure and simple, the human senses.
De facto, this survey will serve to give more strength (or less) the hypotheses previously raised.
In addition, an attempt will be made to form an idea about the vibratory behavior of the set that will guide the use of measuring equipment.
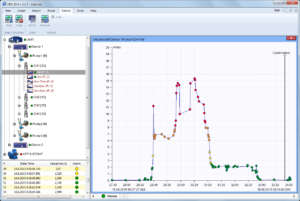
Take, for example, the overall vibration levels measured on a motor pump.
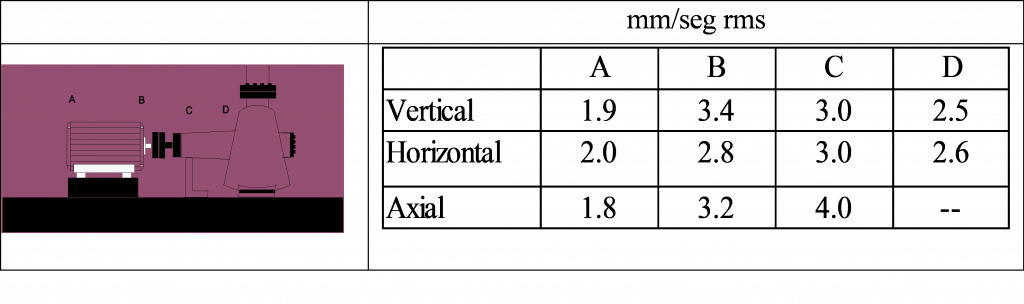
The observation of global levels shows:
- Strong vibrations in the axial direction
- The motor vibrates more vertically than horizontally
- The amplitudes are greater near the coupling
So in these circumstances the main suspect is misalignment in the coupling.
Next, we will look at the frequency spectrum to try to confirm this suspicion and try to increase the probability of success of our misalignment diagnosis as a cause of vibrations..
5.4 Perform visual inspection
So at this stage, will check if “it's all right” and check grips, leaks, etc.
Therefore, in this phase we will try to eliminate the simplest hypotheses and define what the measurement points will be.
5.5 The use of measuring equipment
As is known in the diagnosis by vibration analysis, usually the technique that is first used, is the Frequency Spectrum Analysis.
actually, the raison d'être of this way of acting is to allow identifying the(s) frequency(s) predominant(s) of the vibratory phenomenon, thus making it possible to significantly reduce the list of possible causes.
However, this technique is frequent, by itself, does not make it possible to identify unequivocally which fault.
Like this, what distinguishes the Vibration Analysis specialist, other technicians with experience in maintenance, only stands out at this stage.
De facto, through in-depth knowledge of the various techniques at your disposal, you know which ones to apply in each situation.
Thus, the implementation of other techniques and tests always takes place in order to reduce the number of possible anomalies. In parallel, it is also intended to confirm, by other means, the conclusions reached. De facto, in the latter case, it is intended to increase the degree of certainty of the conclusions.
6 – ELABORATION OF CONCLUSIONS IN DIAGNOSIS BY VIBRATION ANALYSIS
Like this, the coach’s goal is that, when measurements and tests are concluded, has determined, beyond doubt, what is the cause of the anomaly. Now, however, this is very often not the case, arising, therefore, some relevant aspects.
Thus, before drawing a definitive conclusion, the technician has to ensure several aspects:
- That in addition to the faults already considered there are no others that can cause the same symptoms.
- That no relevant aspect was left out of his reasoning.
- That did not funnel your reasoning. Sometimes assumptions “aprioristic” can prevent reasoning from taking the most logical path.
- That there is no evidence to point in other directions. Sometimes we are tempted to fit reality into our thinking, forgetting relevant aspects, instead of reasoning trying to apprehend reality.
Finally, the technician has to estimate the degree of certainty of his conclusions.
The importance of Ockham's scraper in the diagnosis by vibration analysis
More or less, this principle postulates that of multiple adequate and possible explanations for the same set of facts, one must opt for the simplest of those. “Simple” means one that contains the smallest possible number of variables and hypotheses with logical relations between them, of which the fact to be explained follows logically.
This principle was adopted by the scientific method. It is a logical tool that allows you to choose, between several hypotheses to be verified, one that contains the least number of unstated statements, which facilitates the verification of the theory.
summing up: the simplest explanation, is often the most likely.

Figure - Guilherme de Ockham - 14th century philosopher
7 DIAGNOSIS BY VIBRATION ANALYSIS – THE TRANSMISSION OF THE CONCLUSION
Whoever performs diagnosis by vibration analysis in their daily lives must always keep in mind that there is statistical certainty that, On occasion, make a mistake. So when the conclusions reached, this must always be present. De facto, this is all the more important the less familiar with the techniques used, are the people who receive the results of the work.
De facto, the worst thing that can happen to a technician, is to issue a diagnosis about a machine malfunction, with a high degree of confidence, e, later, nothing is indicated.
That way, Among other things, the transmission of the conclusion should also include your degree of confidence. Like this, if an unequivocal conclusion has been reached, the result of the diagnosis can be transmitted in a very affirmative way. On the other hand, if not, words like “one can infer”, “probably”, “perhaps”, or similar, must be used.
Similarly, if there is no certainty of a single cause, the different hypotheses and probability associated with each.