Vibration analysis of clearances and shocks
1 – Vibration analysis of clearances and shocks – Introduction
A Vibration Analysis of clearances and shocks, common vibration analyzer, on a machine is an important preliminary to a maintenance intervention. The gaps and shocks are very common and generate excessive vibrations in the machines. Therefore, anyone who wants to understand the dynamic behavior of equipment in operation must have a reasonably complete understanding of this phenomenon.. This is essential to successfully implement a program of predictive maintenance.
Breaks and their various consequences, are one of the most common anomalies in a park of machines in operation. Having your diagnosis some particularity, it is important to understand its consequences and symptoms.
2 -Consequences of days off
2.1 – Imbalance
Excessive slack and looseness can manifest in a number of different ways..
One consists of generating an imbalance as seen in Fig..
Backlash allowing the axis of inertia of the shaft to become eccentric with respect to the axis of rotation will generate an imbalance.
Under these conditions to distinguish the backlash effect from a pure and simple unbalance of the shaft, you have to look at the previous history of the machine. If the machine has come from a processing facility where clearances were verified, there is suspicion of rotor imbalance., if it's been working for years, is suspicious of days off.
When clearances are high, you can sometimes see the relative movement of the shaft with the bearing, with a strobe.
2.2 – Shocks and Amplitude Oscillations
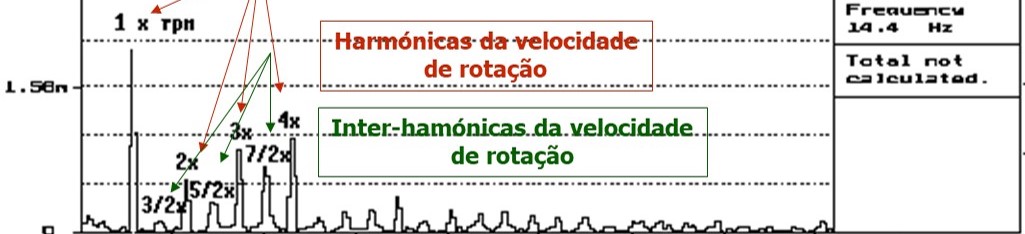
Another way slacks manifest themselves is in the form of shocks.. effectively, sometimes, when the gaps are created, the rotor gains freedom of movement that sometimes leads it to hit the static parts as can be seen in the figure.
In this conditions, in the frequency spectrum, numerous harmonics appear, and sometimes, inter-harmonics of rotational speed.
Note that the most normal spectrum in a fan consists almost exclusively of the component at the rotation speed, which is clearly not the case in fig.. 3.
The interharmonics of the rotational speed constitute, under any circumstances, a clear symptom of the existence of shocks.
In the time base signal the phenomenon becomes evident especially when measured in acceleration.
These shocks are clearly audible with a stethoscope, or more simply with a screwdriver.
2.3 – Incorrect positioning
In case the assembly of a machine is carried out with tight tolerances, the clearances give rise to misalignments, wrong gear etc. The symptoms are, therefore, those of these anomalies, often accompanied by other symptoms of slack such as, for example, imbalance.
3 – unaware
When a machine is loosened from its fixation, there is normally an increase in the amplitude of vibrations., often with the vertical direction as predominant. When the loosening is at the level of the legs, a sensory control to determine whether the amplitude of vibrations in the head of the leg is equal to that of the leg, is usually sufficient to determine whether this is actually the cause.
The strobe can also be used for the same purpose..
4 – SUMMARY OF SYMPTOMS AND TECHNICAL CONSEQUENCES
The table below shows a summary of the consequences., slack symptoms and techniques, shocks and loosenings.